Soccer Player Diet – Workout And Diet Plan For A Soccer Player
A soccer player diet is crucial for optimal performance on the field. It should give you the energy, nutrients, and water needed to build stamina, strengthen, and recover. Because everyone has different needs, you should pay attention to how your body reacts to different things and change what you eat based on that.
Training diet for a soccer player

A well-designed training diet for soccer players is crucial to support their energy needs, optimize performance, and aid recovery. Here are some key considerations for a training diet tailored to soccer players:
Caloric Intake
Football demands a lot of energy. Both training and matches require calories, so players should eat plenty. Individual calorie needs vary by age, weight, position, and workout intensity.
Macronutrient Distribution
Football players get their energy from carbohydrates. Muscle repair and rehabilitation require protein. Avocados, almonds, and olive oil are healthful fats, but fat intake should be limited.
Hydration
Dehydration can decrease performance and increase injury risk, thus enough fluid intake is essential. Football players should drink fluids throughout the day and during training and matches. Electrolyte-rich liquids may be needed during hard exercise, but water is usually plenty.
Timing of Meals
To store energy, eat a carbohydrate-rich meal 2-3 hours before training or a game. Post-training or match meal: Eat carbs and protein within 30-60 minutes to replenish glycogen and heal muscles.
Snacking
Snacks between meals can help maintain energy levels. Opt for nutrient-dense snacks like fruit, yogurt, nuts, or whole-grain crackers.
Vitamins and Minerals
A varied diet of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains delivers vitamins and minerals for health and performance. After seeing a sports nutritionist, players may supplement.
Recovery Nutrition
Including a mix of carbohydrates and protein in post-training or post-match meals and snacks is vital for muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment.
See Also: High School Soccer Field Dimensions
What to eat before a soccer game?
Eating something before a game can have a big effect on how well a player does. Here is a full list of foods that football players should eat before the game.
Pre-Game Meal (2-3 hours before the game)

Carbohydrates:
Choose complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, brown rice, quinoa, or pasta. These provide a sustained release of energy. Include foods like sweet potatoes or legumes for additional fiber and energy.
Lean Protein:
Opt for lean protein sources like grilled chicken, turkey, fish, or tofu. Protein supports muscle function and repair.
Vegetables:
Include a variety of colorful vegetables for essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Hydration:
Drink water to ensure proper hydration leading up to the game.
Sample Pre-Game Meal:
Grilled chicken breast with quinoa and roasted vegetables. Whole-grain pasta with tomato sauce, lean ground turkey, and a side of steamed broccoli.
Pre-Game Snack (30-60 minutes before the game)

Easily Digestible Carbohydrates:
Choose simple, easily digestible carbohydrates to provide a quick energy boost. Examples include a banana, an energy bar, or a piece of toast with honey.
Moderate Protein:
Include a small amount of protein to help sustain energy levels. Yogurt, a small protein smoothie, or a handful of nuts can be good options.
Hydration:
Continue to drink water to stay hydrated. Avoid excessive amounts to prevent discomfort during the game.
Sample Pre-Game Snack:
Banana with a small handful of almonds. Energy bar with a bottle of water. Whole-grain toast with peanut butter.
See Also: Maradona Soccer Move
What to eat and drink during a soccer game?
Eating and drinking during games is essential to maintain energy levels, support performance, and prevent dehydration. Here are some guidelines for what to consume during soccer games:
Food

- Carbohydrates:
- Opt for easily digestible carbohydrates to provide a quick energy source. Examples include energy gels, chews, or sports drinks with carbohydrates.
- Snack Options:
- Energy bars: Choose those with a good balance of carbohydrates and some protein for sustained energy.
- Bananas: A natural source of carbohydrates, and potassium, and easy to digest.
- Raisins or other dried fruits: Quick sources of energy.
- Low-fiber, easily digestible fruits: Consider options like apple slices or oranges.
- Avoid Heavy Foods:
- Steer clear of heavy or high-fat foods, as they can cause discomfort and sluggishness.
Fluids

- Water:
- Consume water at regular intervals during breaks in the game to prevent dehydration.
- Sip water consistently throughout the match, especially in hot and humid conditions.
- Sports Drinks:
- In longer matches or intense conditions, consider sports drinks that contain electrolytes (sodium, potassium) to replace those lost through sweat.
- Sports drinks can also provide carbohydrates for energy during extended periods of play.
- Coconut Water:
- A natural source of electrolytes, coconut water can be an alternative to sports drinks for hydration.
See Also: Soccer Fun Facts
Essential Nutrients for a Soccer Player

Macronutrients
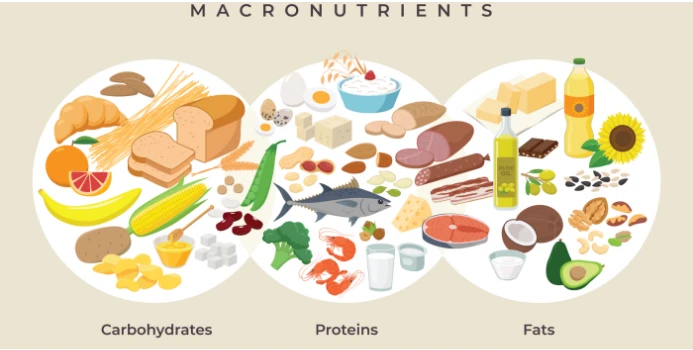
- Carbohydrates:
- Role: Primary energy source for soccer players.
- Sources: Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Proteins:
- Role: Support muscle repair and growth, important for recovery.
- Sources: Lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, beans, and nuts.
- Fats:
- Role: Provide sustained energy, support cell structure, and aid in nutrient absorption.
- Sources: Healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish.
Micronutrients

- Vitamins:
- Vitamin A: Supports vision and immune function. Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin C: Aids in collagen formation and immune support. Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers.
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health and immune function. Sources include sunlight, fatty fish, and fortified dairy.
- Minerals:
- Calcium: Essential for bone health. Found in dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk.
- Iron: Vital for oxygen transport in the blood. Sources include lean meats, legumes, and dark leafy greens.
- Magnesium: Supports muscle and nerve function. Found in nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Zinc: Important for immune function and wound healing. Sources include meat, dairy, and nuts.
Hydration Needs

- Water:
- Adequate hydration is crucial for optimal performance.
- Drink water regularly throughout the day and consider factors like temperature and intensity of training.
- Rehydrate with water during and after training sessions to replace fluids lost through sweat.
- Electrolytes:
- Especially important in hot and humid conditions.
- Sources include sports drinks, coconut water, and certain fruits like bananas.
workout plan for a soccer player in a day
Morning Session (Cardiovascular and Skill Training)

A 15-minute warm-up should include light running and dynamic stretching. Cardio for 30 minutes with interval running and agility drills follow. A 30-minute skill drill on ball control, passing, receiving, and dribbling follows. Cool down with 10 minutes of easy running and static stretching.
Afternoon Session (Strength and Conditioning)

Warm up with jumping jacks, high knees, and dynamic stretches for 10 minutes. A 45-minute strength training program includes squats, lunges, deadlifts, and core exercises. Then do 20 minutes of HIIT and 15 minutes of flexibility and mobility. Cool down with 10 minutes of easy running and static stretching.
Evening Session (Soccer-Specific Drills)

Use shooting, defensive, and small-sided games to improve tactical awareness in a 45-minute session. Then play intense 5v5 or 7v7 games for 30 minutes to build endurance and speed. Cool down with 15 minutes of gentle running and dynamic stretching.
FAQs
Soccer players typically consume a balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, lean proteins, and vegetables to fuel their energy needs.
A regular soccer player’s diet includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fluids to support performance and recovery.
Soccer players generally eat around 3,000 to 5,000 calories per day, depending on factors like their position, training intensity, and individual metabolism.
Yes, soccer players often prioritize protein intake to aid muscle repair and development, with recommended amounts ranging from 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight.
conclusion
Soccer player diet is a critical aspect of their overall performance and well-being. By understanding the specific demands of the sport, crafting a well-balanced diet, and avoiding common mistakes, players can elevate their game and maintain longevity in their careers. Nutrition is not just about fueling the body; it’s a strategic tool for success on the soccer field.